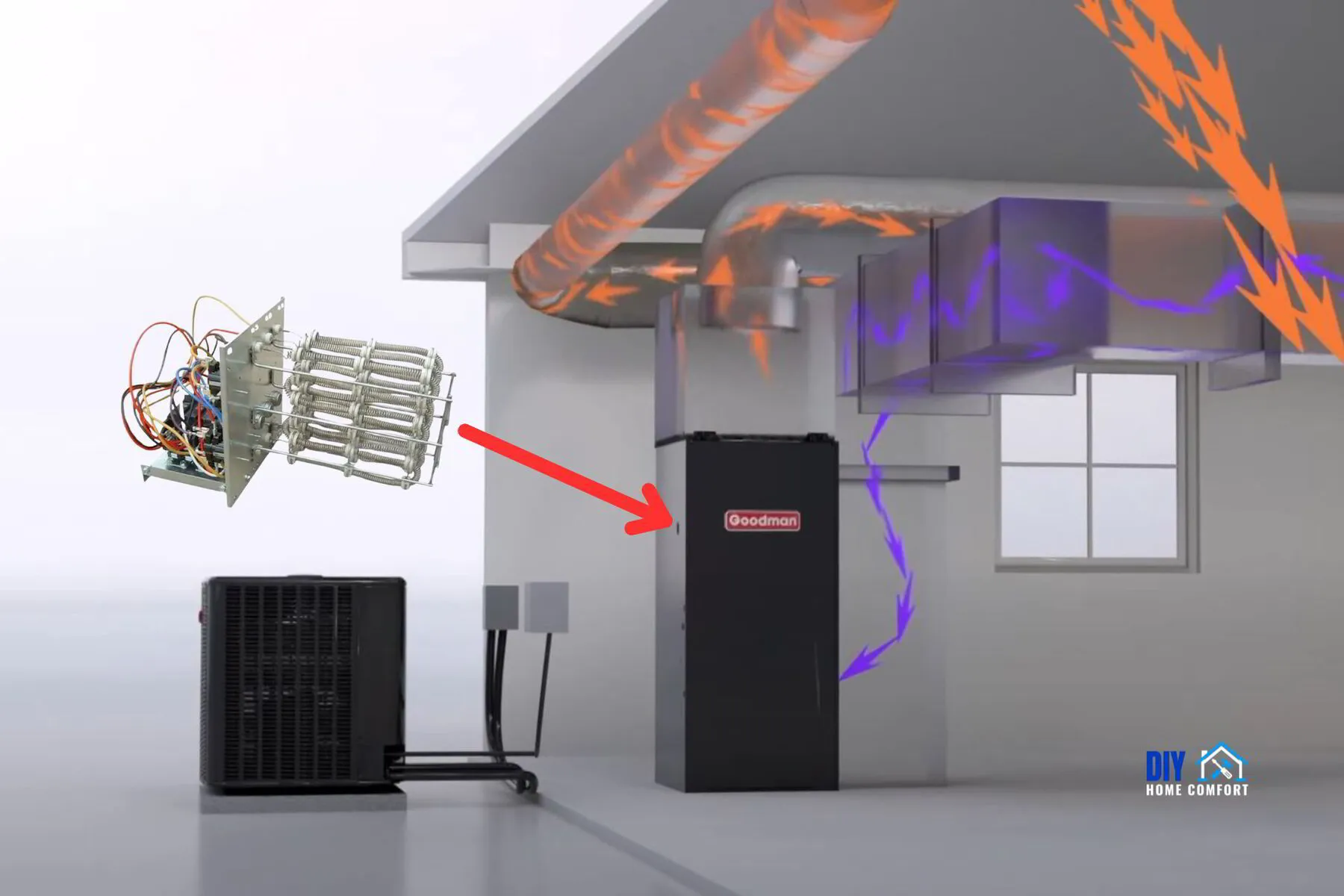
Imagine a chilly winter night. Your heat pump works tirelessly to keep your home cozy, but the outside temperature is plummeting.
Suddenly, the heat pump alone isn’t enough. Enter heat strips, the unsung heroes that step in when the cold becomes too much for the heat pump to handle alone.
📘 Key Takeaways
- Heat Pump Support in Cold Weather: Heat strips are crucial for heat pumps, providing auxiliary or emergency heating when external temperatures fall drastically, typically below 40 degrees Fahrenheit (4.4°C).
- How Heat Strips Work: Operating like a toaster, heat strips generate heat through electrical resistance, converting cold air into warm air, thus maintaining indoor warmth during severe cold.
- Efficiency Maximization Tips: For optimal operation, maintain thermostat settings around 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20°C) and make gradual temperature adjustments to avoid unnecessary activation of heat strips and conserve energy.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: Heat strips offer reliable supplemental heating but can lead to higher energy consumption and potential uneven heat distribution.
- Regular Maintenance Importance: To ensure efficiency and longevity, heat strips require regular maintenance, including inspections for damage, cleaning filters, and checking for proper functionality.
Understanding Heat Pump Heat Strips
Heat strips are a dependable ally to your heat pump, providing support during extremely cold temperatures.
They serve as an auxiliary or emergency heat source, getting into action when the exterior temperature drastically falls, and the heat pump fails to heat your space adequately using just the outside air.
As the exterior temperature changes, the air conditioning system fan circulates air over the heat strips, spreading heat across your home.
When the thermostat setting is increased by more than a few degrees at once, indicating a need for extra heat, the heat strips come into action. In this air conditioning mode, the system efficiently maintains the desired temperature.
Electric Heat Strips: How They Work
An electric heat strip works like a toaster, generating heat through electrical resistance. When electricity flows through the resistive elements, the encountered resistance generates heat.
Constructed using materials such as an electric heating element, insulation materials, and a metal housing, electric heat strips are designed to provide additional warmth when needed.
The heat produced warms the cold air flowing over the heated wire elements, transforming it into warm air, which is then distributed across the house. This ensures that your home remains a haven of warmth when the temperature drops.
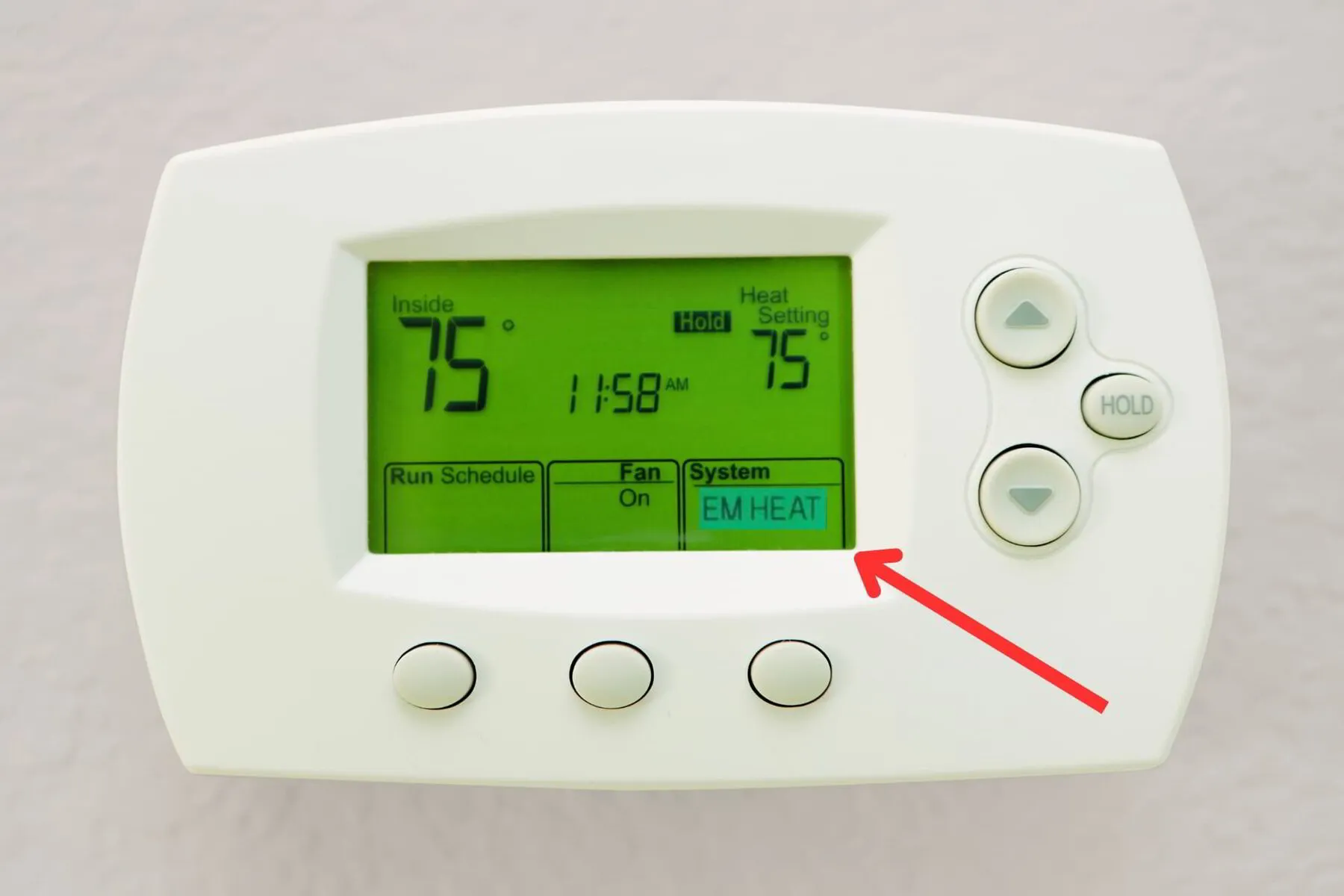
Auxiliary Heat Strips vs. Emergency Heat
What differentiates auxiliary heat strips from emergency heat?
While auxiliary heat strips spring into action when your heat pump needs some help during those cold snaps, becoming active when the outdoor temperature drops to approximately 40 degrees (4.4°C), emergency heat is your safety net when the heat pump malfunctions.
Emergency heat can be seen as a backup plan, a temporary measure when the heat pump malfunctions. It’s like the spare tire in your car, not to be used for long journeys or high speeds but essential when you have a flat. Remember, it utilizes more energy than your standard heat pump or auxiliary heat strips.
📘 Related Reading: When Does a Heat Pump Switch to Emergency Heat?
Maximizing Efficiency with Heat Strips
Now that we understand heat strips and their activation conditions, how can we ensure their optimal operation?
Two key strategies are maintaining optimal thermostat settings and making gradual temperature adjustments. Consider these cardinal rules for enhancing the efficiency of your heat strips.
You balance comfort and energy efficiency by setting your thermostat in the mid-to-high 60s, particularly around 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20°C) during winter.
Gradual temperature adjustments allow your heat pump to operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and preventing unnecessary activation of heat strips.
Smart thermostats can also enhance heat strip efficiency by analyzing activity patterns, making informed temperature adjustments, and providing energy usage insights.
Optimal Thermostat Settings
With the thermostat set at 68 degrees during the day, dependence on heat strips minimizes, thereby striking a balance between comfort and energy efficiency.
When you’re asleep or away from home, setting it at 65 degrees (18.3°C) helps conserve energy and limit the use of heat strips.
These thermostat settings offer several benefits:
- Achieving a balance between comfort and energy efficiency
- Minimizing the need for supplemental strip heating
- Ensuring the energy-efficient operation of the heat pump
Maintaining consistent, appropriate settings, including the heat mode, is key to optimizing the heat strips’ performance.
Gradual Temperature Adjustments
Consider your thermostat as a volume knob rather than a switch when adjusting the temperature. Gradual adjustments prevent the activation of heat strips, enabling the heat pump to extract heat from the outside air.
Incrementally raising the thermostat by two degrees is the most effective method for increasing the temperature in a home equipped with a heat pump system.
This approach allows the heat pump to heat the space without using auxiliary heat strips, reducing energy consumption and improving the efficiency of the heat pump system.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Heat Strips
Heat strips, like any heating solution, have advantages and drawbacks. On the benefits side, they’re a dependable supplemental heating source that delivers necessary warmth during colder seasons and is conveniently installed.
On the downside, heat strips can lead to increased energy consumption and uneven heat distribution.
Advantages: Cost-effective and Reliable Supplemental Heating
Heat strips serve as a cost-effective and reliable backup heating source. They complement the heat pump, which is known for its cost efficiency, especially during sub-freezing conditions.
While heat strips consume more energy, they still present an economical supplemental heating solution. They may have higher initial costs, but their cost-effectiveness should be assessed regarding long-term efficiency and operational expenditures.
In icy weather conditions, heat strips can become more efficient as heat pumps may not be able to provide warmth on their own adequately.
In such situations where the temperature falls below the heat pump's effective range, heat strips function as an efficient supplementary heat source to meet the heating requirements.
Disadvantages: Energy Consumption and Uneven Heat Distribution
Higher energy consumption of heat strips compared to a heat pump can lead to elevated energy bills. So, while they provide extra warmth when you need it, they could also lead to an unexpected utility bill spike.
Heat strips may also result in the following:
- Uneven heat distribution
- Creation of a localized heat source
- Reliance on convection currents to circulate the air may prove less effective in larger rooms or spaces with complex layouts.
Heat Strip Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Frequent maintenance and troubleshooting can ensure your heat strips remain in optimal condition. Just like your car needs regular oil changes, your heat pump and heat strips need regular care to stay efficient and effective.
Here are some steps you can take to maintain your heat strips:
- Schedule inspections for damage or overheating.
- Examine the pump’s exterior for any signs of wear or damage.
- Inspect electric terminals for any loose connections or corrosion.
- Use an amp meter for strip testing to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Clean or replace filters as required to maintain good airflow.
By following these steps, you can keep your heat strips in good working condition and ensure efficient heating in your home.
Understanding common issues and their solutions can prevent unnecessary headaches and save troubleshooting time.
Frequent issues may encompass:
- Inadequate heat output from the air handler
- poor performance of the heat pump
- unpleasant odors
- continuous operation of the heat strips
- water accumulation near the unit
Regular Maintenance for Optimal Performance
Annual servicing is crucial to maintain the optimal performance of your heat strips.
- Regular maintenance ensures:
- Proper functionality
- Prevention of unforeseen malfunctions
- Smooth operation of the heat pump over time
- Extension of the lifespan of the heat strips.
Standard maintenance procedures for a heat pump involve:
Regular inspections for indications of damage, corrosion, or overheating
Examining for blockages and debris
Assessing the exterior of the heat pump
Inspecting electric terminals for cleanliness and secure connections
Checking for refrigerant leaks
Key indicators that your heat strips may require maintenance include:
- Inadequate heat output from the air handler
- Subpar performance of the heat pump
- A musty or soiled sock odor
- Continuous operation of the heat strips
- The presence of water near the unit
Identifying and Resolving Noise Issues
Heat strips can sometimes make a lot of noise. If you’re hearing buzzing, resonances, clunking, banging, or clicking noises, it could be due to a number of issues, such as unplugged low-voltage connectors, poor pipe support, scale accumulation on the heat exchanger, or an electrical fault.
A blocked blower wheel can also lead to significant noise issues. It can cause vibrations, thumping sounds, or squeaking noises due to disrupted balance and increased friction.
To address these noise problems, you can verify the cleanliness and proper installation of the air filter, utilize rubber pads beneath the unit to absorb vibrations and diminish noise, and adjust the positioning of the heat strip heating system.
📘 Related Reading: Heat Pump Noises - The Good and the Bad
Choosing the Right Heating Solution for Your Home
Selecting a decent heating solution for your home requires thoughtful consideration of multiple factors. It’s a bit like buying a car; you wouldn’t just go for the first shiny model you see.
You’d consider the fuel efficiency, the cost, the size, and how it fits your specific needs. Likewise, selecting a heating solution necessitates the consideration of elements like your home’s heating requirements, the local climate, and energy efficiency objectives.
While heat strips could be a suitable choice for certain homes, they may not be the ideal solution for all. This is where the role of alternative heating solutions comes into play.
There are several other heating options out there, such as:
- Electric water heaters
- heat pumps
- underfloor heating
- smart thermostats
- solar panels
- biomass boilers
- infrared heating panels
- passive solar heating.
📘 Related Reading: The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of Heating Systems
Factors to Consider
There are several aspects to consider when choosing the right heating solution for your home. Think about how heat strips perform in various climates.
Heat strips may be crucial in colder climates to supplement the heat pump's heating capacity. But in milder climates, the heat pump alone may suffice for adequate heating.
Also, consider the size and layout of your home. The efficiency of heat strips can be affected by these factors. Properly sizing the heat pump and strategically placing heat strips can optimize their efficiency.
Additional factors to take into account encompass:
- cost
- energy efficiency
- sustainability
- the size of the rooms that need heating.
Alternative Heating Solutions
If heat strips appear unsuitable for your home, there’s no need to worry. There are plenty of alternative heating solutions to explore.
Alternatives include:
- Solar heating systems
- Geothermal heating systems
- Radiant floor heat
- Hybrid furnaces
- Wood stoves
- Pellet stoves
- Electric hydronic baseboard heaters
- Hydronic radiant floor heaters
Each of these options has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, a furnace heating system can provide rapid heating and is cost-efficient, but it might have higher initial costs and increased maintenance requirements.
On the other hand, a boiler heating system offers higher heat output and energy efficiency but might have a complex and noisy installation process and a higher initial cost.
📘 Related Reading: HVAC Insights: How Does a Heat Pump Work in Winter?
Summary
Heat strips are crucial in providing supplemental heat during extremely cold temperatures.
They are a reliable backup when the heat pump alone can’t keep up with the heating demand. However, like any heating solution, they have their pros and cons.
They aren’t always the most energy-efficient option and can lead to uneven heat distribution. Regular maintenance and proper usage can help optimize their performance and prolong their lifespan.
When choosing the right heating solution for your home, consider factors like your home’s heating needs, local climate, and energy efficiency goals, and don’t shy away from exploring alternative heating options.
Want to learn more about your HVAC system? Check out our other HVAC articles!
Scott Harding
Scott is the main author of DIY Home Comfort. He's also an experienced HVAC technician that enjoys home renovation and spending time with his family. You can find out more about him here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do heat strips work in a heat pump?
Heat strips in heat pumps provide supplemental heating when temperatures drop, typically activating around 35 degrees Fahrenheit (1.6°C), but this threshold varies. They operate as needed, not constantly.
What turns on the heat strips in a heat pump?
The electric heat strips in a heat pump are usually triggered to turn on if the system runs for more than 15 minutes without raising the temperature more than half a degree.
Do heat strips use a lot of electricity?
Heat strips typically uses 1000 watts of electricity, however the wattage may vary depending on the size and brand. As such, heat strips can use a lot of electricity.
How do you know if heat strips are bad?
If you're not getting enough warmth, this could be a sign that your electric heat strips are malfunctioning or the wiring is having an issue.
When to use emergency heat?
Emergency heat should be used when the outside temperature is too cold for the heat pump to keep your home warm or if the heat pump has been damaged. Switching to emergency heat and calling an HVAC service provider is advised in such cases.