Experiencing the sudden shock of cold water during a relaxing shower or while doing your dishes can be frustrating. This issue of rapid hot water depletion is one that many homeowners encounter. Fortunately, it's a problem with solutions.
I'm Scott Harding, a seasoned expert in home plumbing systems with over 15 years of experience in the industry. In this article, we delve into the common causes of hot water shortages and offer you practical, tried-and-tested solutions to prevent these issues.
Drawing from my extensive plumbing and home maintenance background, I'll guide you through understanding and resolving these challenges effectively.
📘 Key Takeaways
- Diverse Hot Water Systems: Gain an understanding of different hot water systems, including tank, tankless, solar, and heat pump models, and their specific operational mechanisms.
- Root Causes of Depletion: Identify common causes of rapid hot water depletion, such as sediment buildup, faulty heating elements, damaged pipes, and high usage patterns.
- Maintenance and Prevention: Recognize the importance of regular maintenance, like tank flushing, and proactive measures to prevent future hot water shortages.
- Solutions and System Upgrades: Explore effective solutions for immediate issues and consider upgrading to more efficient systems for long-term benefits.
- Expert Insights for Optimal Selection: Utilize expert advice to choose the right hot water system tailored to your household's needs, ensuring consistent hot water availability.
Understanding Your Hot Water System
How Do Hot Water Systems Work?
Hot water systems function by heating water and then delivering it to your faucets and appliances. The process varies slightly depending on the type of system but generally involves heating water through a dedicated heating element and then storing or directly supplying this hot water as needed.
Types of Hot Water Systems
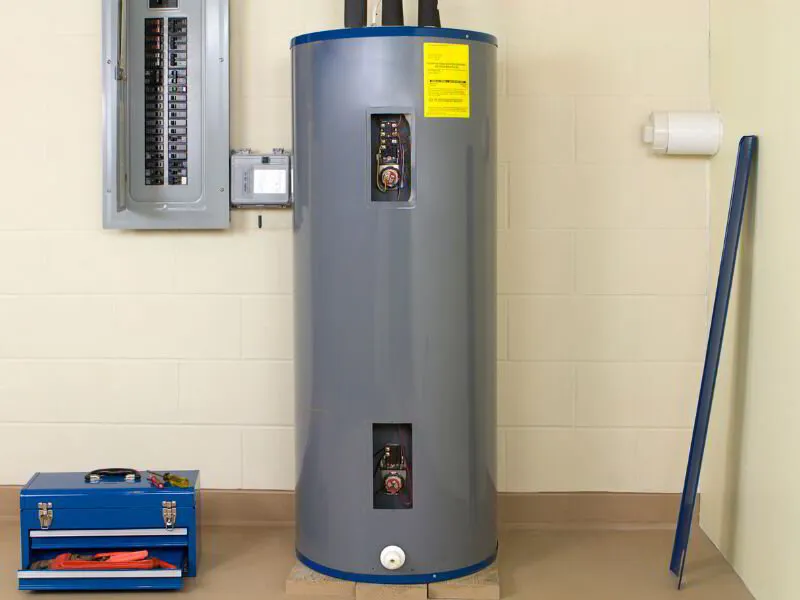
- Tank Water Heaters: These systems heat water stored in a large tank. When you turn on the hot tap, hot water from the top of the tank is replaced by cold water at the bottom, which is then heated.
- Tankless Water Heaters: These provide hot water on demand by heating water directly as it flows through the system, eliminating the need for a storage tank.
- Solar Water Heaters: Utilizing solar panels, these systems capture solar energy to heat water, which is stored in a tank for later use.
- Heat Pump Water Heaters: These systems use electricity to move heat from the air or ground to heat water rather than generating heat directly.
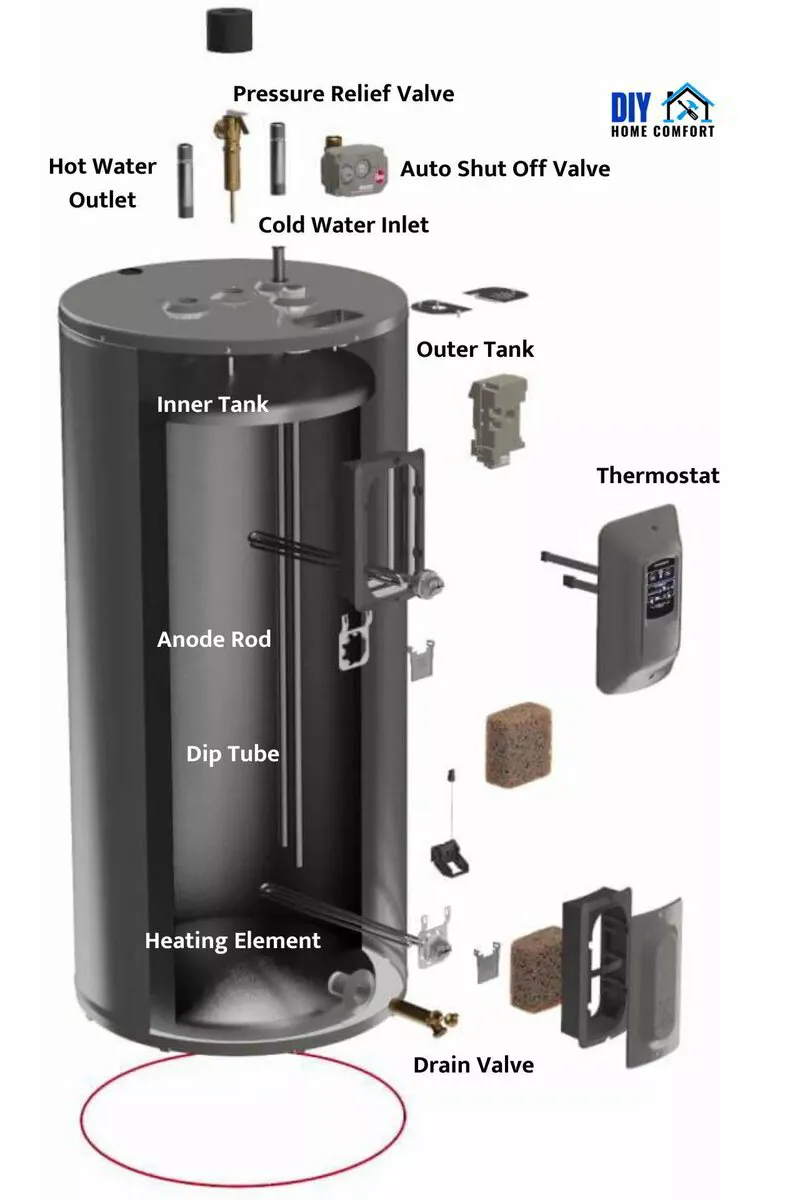
Key Components and Their Functions
Understanding the various components of your hot water system is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Here's a breakdown of the key components commonly found in most hot water systems:
- Heating Element: In tank water heaters, this is either a gas burner or an electric element that heat the water. In tankless systems, the heat exchanger rapidly heats the incoming water.
- Thermostat: A control device that regulates the water temperature in the tank, ensuring it stays within a safe and desired range.
- Dip Tube: Directs incoming cold water to the bottom of the tank, where it gets heated, ensuring efficient operation.
- Heat-Out Pipe: Allows the heated water to exit the tank and flow to your faucets and appliances.
- Pressure Relief Valve: A safety feature that releases pressure if it gets too high inside the tank, preventing potential damage or explosions.
- Drain Valve: Located near the bottom of the tank, used for draining the tank during maintenance or repairs.
- Anode Rod: A sacrificial rod that helps prevent corrosion inside the tank. It's particularly crucial in tank water heaters.
- Expansion Tank: Used in some systems to absorb excess pressure due to thermal expansion in closed water systems.
- Temperature and Pressure (T&P) Relief Valve: Releases water if the temperature or pressure inside the tank is too high.
- Venting System: In gas water heaters, this component safely expels combustion gases produced by the burner.
- Pilot Light or Ignition System: This component is responsible for igniting the gas burner in gas heaters.
- Circulation Pump: In certain systems like solar water heaters, this pump circulates water or a heat-transfer fluid through the system.
- Insulation: Surrounds the tank to help retain heat, keeping the water hot for longer periods and improving energy efficiency.
- Control Panel: In modern tankless systems, this electronic interface allows users to adjust settings and monitor system performance.
- Cold Water Shut-off Valve: Controls cold water flow into the system, allowing for maintenance or emergency shut-off.
- Hot Water Outlet: The point from which hot water exits the tank and is distributed to the house.
By familiarizing yourself with these components and their roles, you can better understand how your hot water system operates, diagnose issues, and perform routine maintenance. This knowledge is essential for maintaining your home's reliable and efficient hot water supply.
Maintenance for Optimal Performance and Longevity
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of your hot water system. This includes flushing the tank to remove sediment, checking the pressure relief valve, and ensuring the thermostat functions correctly.
- Tank Water Heaters typically last about 10-15 years.
- Tankless Water Heaters have a longer lifespan, often lasting up to 20 years.
- Solar Water Heaters can last between 15-20 years, depending on maintenance and weather conditions.
- Heat Pump Water Heaters generally have a lifespan similar to tankless models, around 15-20 years.
Proper maintenance not only extends the life of your system but also ensures a consistent hot water supply. It's important to note that the lifespan can vary based on the unit's quality, the water's hardness, and how well the system is maintained.
By understanding how your hot water system works, its key components, and the importance of regular maintenance, you can better identify issues, perform routine upkeep, and make informed decisions about system upgrades or repairs.
This knowledge helps avoid the inconvenience of unexpected hot water shortages and ensures efficient operation of your system.
Causes of Rapid Hot Water Depletion
Hot water is essential for many daily activities, including showering, washing dishes, and doing laundry. However, running out of hot water can be frustrating and inconvenient.
There are several reasons why your hot water may run out quickly. In this article, we will explore some common causes of rapid hot water depletion and how to prevent them.
1. Faulty Heating Elements
Heating elements in electric heaters are crucial for warming the water. When these elements deteriorate or fail, they can't heat the water effectively, leading to a swift decline in hot water availability.
This issue is particularly noticeable during high-demand periods, such as morning routines or back-to-back showers.
Solution!
Regularly inspect the heating elements, especially if you notice a drop in water temperature. Replacing faulty elements is key to restoring efficiency. It's advisable to hire a professional to ensure correct and safe installation.
2. Sediment Buildup in the Tank
Minerals like calcium and magnesium in water gradually form a layer of sediment at the bottom of your heater's tank.
This sediment acts as a barrier between the heating element and the water, reducing heating efficiency and tank capacity. Over time, this leads to quicker depletion and less available hot water.
Solution!
Prevent sediment buildup by draining and flushing your water heater annually. This process involves emptying the tank and allowing fresh water to flush out the sediment. For best results, consult a professional for periodic maintenance.
3. Broken Dip Tube
The dip tube in your water heater directs cold water to the bottom of the tank for heating. If this tube is broken or cracked, cold water can mix with the hot water at the top of the tank, rapidly decreasing the overall temperature and availability of hot water.
Solution!
Inspect the dip tube for any signs of damage. This can often be identified by a decrease in water temperature or bits of plastic in your water (if the dip tube is made of plastic).
Replacing a broken dip tube is a relatively straightforward process but may require professional assistance, especially for ensuring correct installation and avoiding future issues.
4. Damaged or Leaking Pipes
Leaks or damage in your hot water system's plumbing can cause significant water loss. This not only leads to wastage but also reduces the volume of hot water available. Leaks often occur in older pipes or at connection points and can be exacerbated by high water pressure or corrosion.
Solution!
Regularly inspect visible pipes for signs of damage or leaks. Early detection and repair of leaks, ideally by a professional plumber, can prevent further damage and restore your hot water supply.
5. High Water Usage
Excessive simultaneous use of hot water appliances and fixtures can rapidly drain your water heater. This is especially problematic in homes with multiple occupants where showers, dishwashers, and washing machines may all be in use at the same time, overwhelming a water heater's capacity to replenish hot water quickly.
Solution!
Implement water-saving strategies like installing low-flow showerheads and aerators. Also, consider scheduling the use of hot water appliances during different times of the day to balance the demand on your water heater.
6. Thermostat Malfunctions
A malfunctioning or improperly set thermostat on your water heater can lead to inadequate heating of water. If the thermostat fails to signal the heater to activate or is set too low, the water may not reach the desired temperature, resulting in a faster depletion of the hot water supply.
Solution!
Regularly check your water heater's thermostat for accurate temperature settings. Resetting or replacing the thermostat can often resolve the problem if you suspect a malfunction. For complex problems, seek professional assistance.
7. Inadequate Water Heater Size
If your water heater is undersized for your household's needs, it will struggle to provide an adequate hot water supply as the demand exceeds the water heater's recovery rate. This is often an issue in growing families or homes with increased hot water demands where the existing water heater capacity is insufficient.
Solution!
Assess your household's peak hot water demands. Upgrading to a water heater with a higher recovery rate or a tankless water heater, which provides instant hot water on demand, can effectively address this issue. This ensures a continuous supply even during high usage periods.
8. Gas Supply Issues (for Gas Heaters)
For gas heaters, disruptions in the gas supply, issues with the burner, or a malfunctioning pilot light can impair the heater's ability to warm water. These problems can stem from external supply issues, component wear, or operational faults, leading to inefficient heating and hot water shortages.
Solution!
Regularly check the gas line, pilot light, and burner. If you suspect a gas supply issue, contacting a professional for safe and effective repairs is crucial, as gas-related problems can be hazardous.
9. Electrical Issues (for Electric Heaters)
Electrical problems, such as tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses, can halt the operation of electric water heaters. These issues often arise from power surges, overloaded circuits, or aging electrical components, resulting in the heater being unable to heat water.
Solution!
Ensure your electrical system is in good condition. Check for tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses, and ensure the heater receives power. For persistent electrical issues, consult with a qualified electrician.
10. Age and Wear of the Water Heater
As water heaters age, their efficiency and effectiveness diminish. Older heaters may have worn-out components, reduced heating capability, and compromised insulation, all contributing to a faster depletion of hot water. Regular maintenance can mitigate some age-related issues, but eventually, replacement may be necessary.
Solution!
Consider the age of your water heater in assessing its performance. If it's nearing the end of its typical lifespan (around 10-15 years), planning for a replacement might be more cost-effective than frequent repairs.
11. Crossed Connections
Incorrect plumbing installations can result in crossed hot and cold water connections. This issue often arises during new installations or renovations and can lead to unexpected temperature fluctuations and reduced hot water delivery, as cold water mixes with the hot water supply.
Solution!
If you experience unexpected temperature fluctuations, have a plumber check for crossed connections. This issue often requires professional correction to ensure proper hot and cold water delivery.
12. Thermal Switch Malfunction (Gas Heaters)
The thermal switch in gas heaters, designed as a safety mechanism to shut off gas if a problem is detected, can malfunction. This can disrupt the heating process, leading to a lack of hot water and potential safety hazards.
Solution!
Regular testing and maintenance of the thermal switch are crucial. If malfunctioning, it should be replaced promptly by a qualified technician to ensure your gas water heater's safe and efficient operation. Regular professional inspections can prevent such issues.
13. Venting Issues (Gas Heaters)
Proper venting is crucial for gas water heaters to expel combustion gases safely. Inadequate or obstructed venting can lead to inefficient heating and potential safety risks, including the buildup of harmful gases.
Solution!
Ensure that the venting system is correctly installed, regularly maintained, and free from blockages. Scheduling annual inspections by a certified professional can help maintain the system's safety and efficiency, preventing venting-related issues.
14. Water Pressure Issues
Water pressure that is too high or too low can adversely affect the water heater's performance. High pressure can strain the system, while low pressure can hinder efficient water flow and heating.
Solution!
Install a pressure regulating valve if the water pressure is consistently high. Check for closed supply valves or clogged pipes for low pressure and clear them. Regular monitoring and adjusting water pressure can prevent these issues and maintain optimal heater performance.
15. Corrosion Inside the Tank
Over time, the water tank can corrode due to mineral deposits and chemical reactions, leading to leaks and reduced heating efficiency. Corrosion can also compromise water quality and the structural integrity of the tank.
Solution!
Regular inspections for corrosion signs are essential. Replacing the anode rod periodically can prevent corrosion. If the tank shows significant corrosion, it's often more cost-effective and safer to replace the entire water heater to ensure reliable and efficient operation.
16. External Cold Temperatures
In colder climates, the incoming water temperature can be significantly lower, requiring more energy and time to heat. This increased demand can strain the water heater's capacity, especially if it's not designed for such conditions, leading to a rapid depletion of hot water.
Solution!
Insulate your water pipes to minimize the effects of cold temperatures. In extremely cold areas, consider a water heater with a higher capacity or advanced features designed for cold climates.
17. Lack of Maintenance
Neglecting regular maintenance of your water heater can lead to various issues that reduce its efficiency. Maintenance tasks like flushing the tank, checking the anode rod, and inspecting heating elements are crucial for optimal operation and preventing rapid hot water depletion.
Solution!
Establish a routine maintenance schedule for your water heater, including periodic inspections, anode rod checks, and system flushes. Regular maintenance can significantly extend the life and efficiency of your heater.
18. System Design Flaws
Inefficient design or installation of your hot water system can cause delivery problems. Issues like long pipe runs, inadequate insulation, or improperly sized systems can all contribute to a lack of hot water when needed, as they affect the system's ability to deliver hot water efficiently.
Solution!
If you consistently face hot water issues, consult with a plumbing expert to review your system's design. Sometimes, redesigning or modifying the existing setup can greatly improve hot water delivery and efficiency.
By understanding these specific causes, you can better identify and address the reasons behind your hot water shortages.
Finally!
Dealing with a hot water shortage can be frustrating, but it's a challenge that can be effectively resolved. Gaining a clear understanding of the various causes behind hot water shortages empowers you to take proactive steps towards prevention.
Engaging in regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of your hot water system. Additionally, considering timely upgrades and adopting water-saving techniques can significantly contribute to a steady and reliable hot water supply in your home, ensuring comfort for you and your family.
Interested in further insights or tips about managing your home's water heating needs? Explore our collection of articles on water heaters for more expert advice and practical solutions.
Scott Harding
Scott is the main author of DIY Home Comfort. He's also an experienced HVAC technician that enjoys home renovation and spending time with his family. You can find out more about him here.